#Product Trends
Surface Treatment Methods for Metal 3D Printing
The main post-processing methods include finishing and mechanical processing
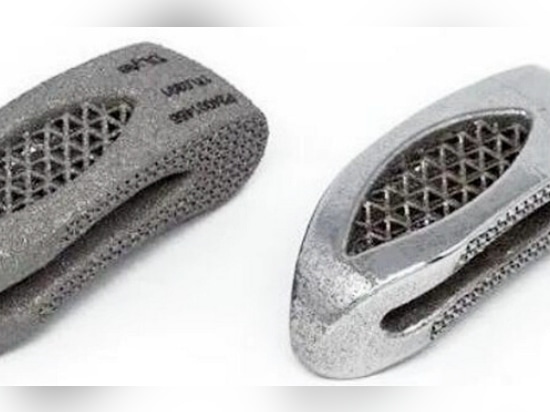
One unsolved challenge in additive manufacturing is surface finish. In theory, additive manufacturing allows complete freedom to create complex shapes, but in practice, surface finish requirements usually require design constraints. Although improving the quality of metal powder, optimizing the building direction and process parameters can improve the surface quality of additive manufacturing parts to a certain extent, the surface roughness problem of additive manufacturing parts cannot be completely solved. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out post-processing of additive manufacturing parts. At present, the main post-processing methods include finishing and mechanical processing.
Finishing methods mainly include hand polishing, sand blasting or numerical control grinding. Manual polishing quality depends largely on the operator's experience, which has poor repeatability and consistency, high labor and time costs, and the dust produced in the polishing process is harmful to human health. In addition, sandblasting and CNC grinding have poor processing accessibility for parts with complex inner surface and porous structure, so they are generally used for cleaning and polishing the outer surfaces of parts and removing the oxide layer.
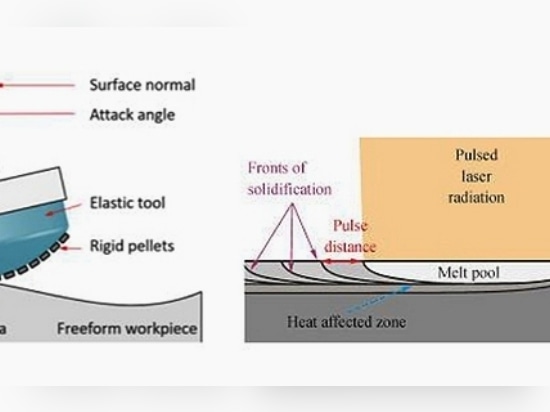
For complex structural parts with high surface quality requirements (0.8μm
1. Shape Adaptive Grinding
Shape Adaptive Grinding (SAG) is a novel process for freeform machining of difficult materials such as ceramics and hard metals. Despite low stiffness equipment from the machining equipment, due to the semi-elasticity of the tools, ductile mode grinding can be achieved with high surface finish. A foreign researcher used the shape adaptive grinding method with spherical flexible grinding head to polish the free-form surface of titanium AM parts. The defect layer on the additive manufacturing surface was removed by rough polishing and fine polishing, and the final surface roughness Ra reached less than 10nm
2. Laser Polishing
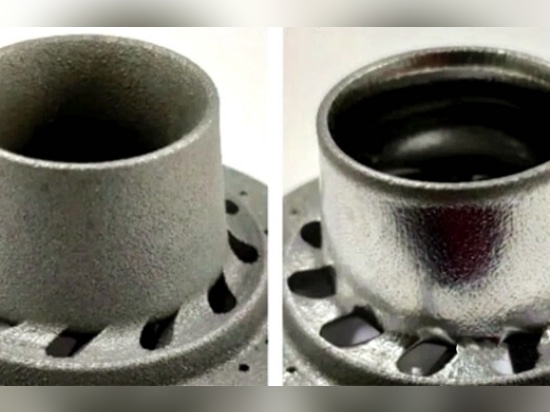
Laser polishing is a new polishing method which uses high-energy laser beam to melt the surface material of parts again to reduce the surface roughness. At present, the surface roughness of laser polished parts Ra is around 2~3μm.Due to the high cost of laser polishing equipment, it has not been widely used in practical 3d printing post-treatment process.
3. Chemical Polishing
The direct result of chemical polishing is micro roughness smoothing and polish formation along with parallel dissolution of an upper layer. It has a remarkable effect on removing the spheroidal layer that is loose and easy to fall off on the surface of hollow structure or parts with hollow structure in small additive manufacturing. Through chemical polishing and electrochemical polishing, the surface roughness of above porous implant was reduced from 6~12μm to 0.2~1μm.
4. Abrasive Flow Machining
Abrasive flow machining (AFM), is an interior surface finishing process characterized by flowing an abrasive-laden fluid through a workpiece. This fluid is typically very viscous, having the consistency of putty, or dough. AFM smooths and finishes rough surfaces, and is specifically used to remove burrs, polish surfaces, form radii, and even remove material. The nature of AFM makes it ideal for interior surfaces, slots, holes, cavities, and other areas that may be difficult to reach with other polishing or grinding processes.
Powder bed fusion technology can achieve the best surface quality among all metal additive manufacturing processes. In addition to the above finishing methods, critical parts sometimes need to be machined. These two kinds of post-treatment means are widely used in the 3d printing mold application. Welcome to contact us to explore more post treatment methods for metal 3d printing.