#Product Trends
What is a Linear Robot?
Different uses for Linear robotics.
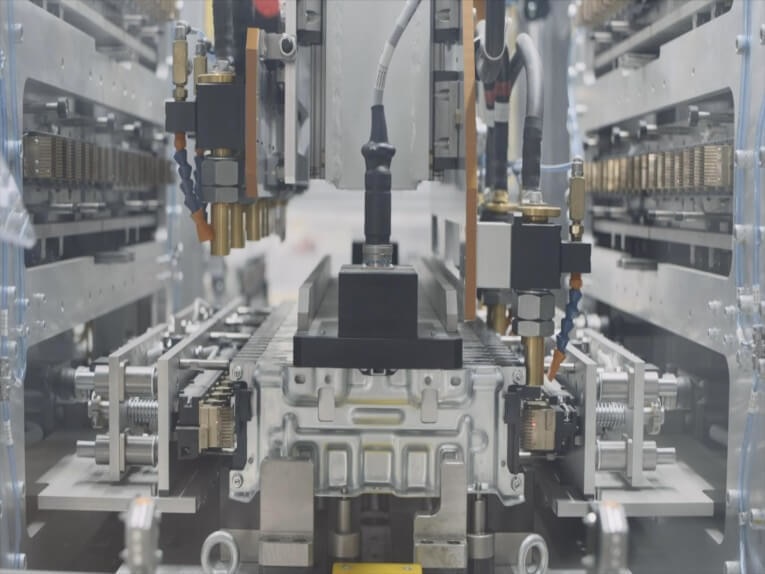
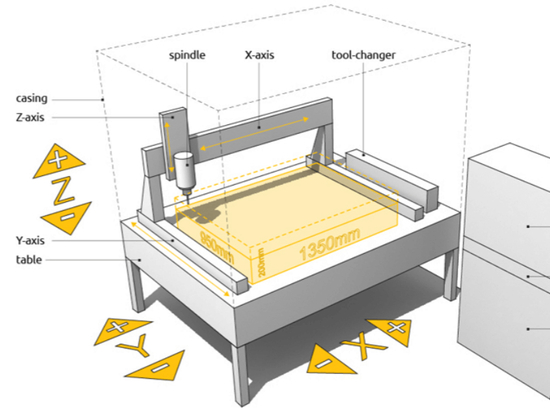
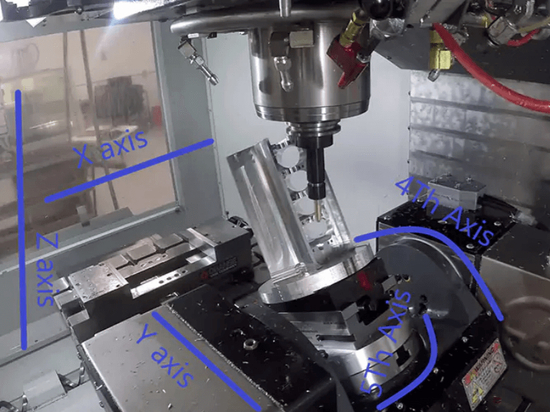
With automation on the rise, the case for linear robotics, has expanded. Linear robots are a type of industrial robot with two or three principal axes that move in a straight line rather than rotate, functioning at right angles to each-other. The three sliding joints correspond to moving the wrist; up and down, back and forth, as well as in and out. Linear robots with horizontal members supported at both ends are referred to as Gantry robots.
Because there are no rotating axes, linear robotics tend to have a higher degree of accuracy, making them the ideal automation solution for those mundane repetitive tasks. Unlike other automation machines, linear robotics systems can be reprogrammed to accommodate product changes quickly, and are flexible to meet unique requirements. A linear robot can be more economical than other types of robots such as articulated arm or SCARA.
Many industries today require automated processes to ensure process repeatability, reduce variability, meet quality expectations and lower manufacturing costs. Automation is vital to many companies to meet lead-time demands and remain competitive. Robotic systems offer the best cost investment as they can be reprogrammed or repurposed to meet product variety and life cycles. Linear robotics are a versatile solutions for these challenges.
There are many different uses for Linear robotics, but the most common are:
Pick and Place Solutions – High-speed pick and place robots move a product from one location to another with spot-on accuracy. Manual errors like placing the wrong item in the wrong place can be replaced with linear robotics. Implementing a pick and place system to place items in certain spots and on assembly lines can greatly improve efficiency and accuracy, as well as prevent injuries.
Sorting – A linear robot can streamline the traditionally manual and monotonous process of sorting, making it more efficient and safer. When coupled to a vision system, accurate distinctions can be made with greater consistency.
Packaging Solutions – Packaging processes can run 24/7 when utilizing a linear robotics system because you can theoretically run even with the lights out! Allowing production to run non-stop would be extremely difficult for laborers to manually handle. This eliminates the need for a 3rd shift crew. This is a great way to improve turnaround time.
Palletizing – A palletizer takes products and places them in a predetermined pattern to form layers and then place them onto a pallet. Without automation, this could be a dangerous heavy-lifting manual job. Robotic systems greatly increase productivity and reliability for palletizing processes. They have a minimal equipment footprint and have become a more ideal solution for a wider range of packaging scenarios.
Assembly Processes – Many processes such as dispensing, cutting, forming, welding etc. are better performed by a Linear Robotic system, especially when long travels and extended reach are required.