#Product Trends
Comparing Ceramic Fiber Blanket with Other Insulation Materials
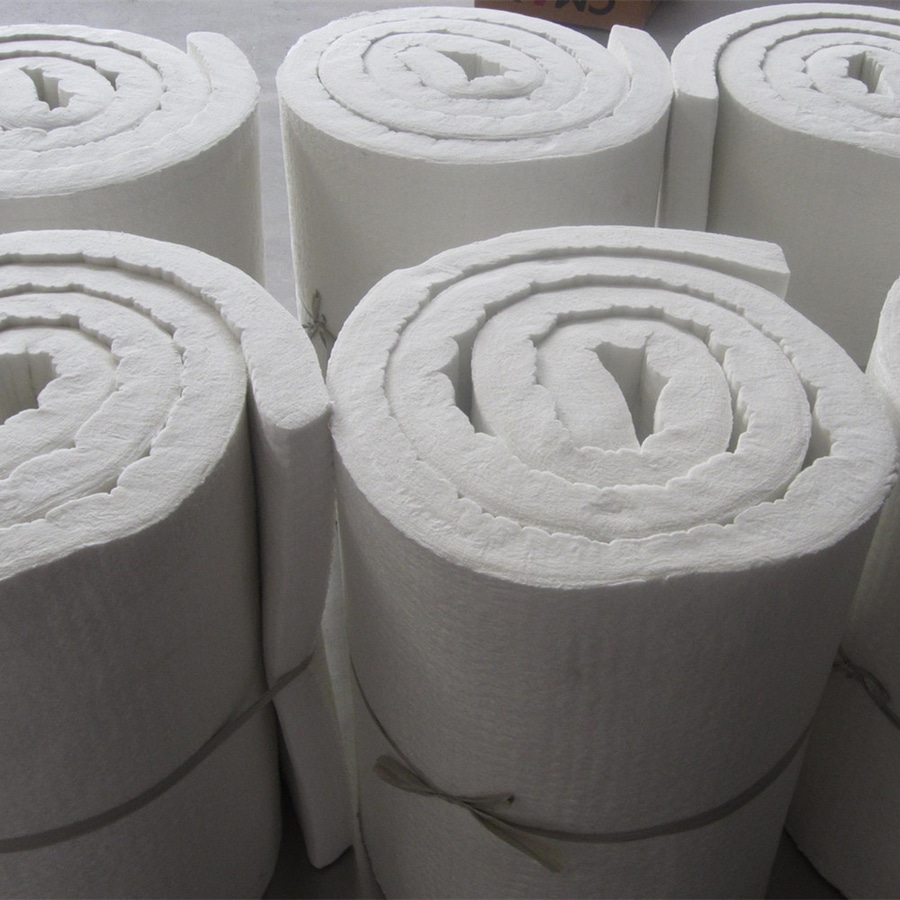
Ceramic Fiber Blanket
When it comes to high-temperature insulation, choosing the right material can make a significant difference in both performance and cost-effectiveness. Ceramic fiber blankets, fiberglass, and mineral wool are all commonly used for thermal insulation in industrial settings. But how do these materials compare when it comes to heat resistance, durability, installation, and overall efficiency? In this post, we’ll break down the key differences between ceramic fiber blankets and other popular insulation materials, helping you make an informed decision for your specific needs.
1. Heat Resistance: The Core Strength of Ceramic Fiber Blanket
Ceramic fiber blankets are designed to withstand extremely high temperatures—up to 2300°F (1260°C)—making them ideal for environments with intense heat, such as furnaces, kilns, and exhaust systems. They provide superior heat retention and stability, even under continuous exposure to high temperatures. In comparison:
Fiberglass typically handles temperatures up to 1000°F (538°C), which makes it suitable for lower to moderate temperature applications. However, it tends to degrade faster in extreme heat compared to ceramic fiber.
Mineral wool offers heat resistance in the range of 1200°F (649°C), but its performance can deteriorate in the presence of high humidity or moisture, making it less reliable than ceramic fiber blankets in some conditions.
For industries dealing with temperatures above the capabilities of fiberglass or mineral wool, ceramic fiber blankets offer superior performance in terms of heat retention and long-term durability.
2. Durability: Long-Lasting Protection
The durability of insulation materials is crucial for minimizing maintenance costs and extending the life of your equipment. Here's how ceramic fiber compares to other materials in terms of durability:
Ceramic Fiber Blanket is highly resistant to wear and tear, even under extreme conditions. Its non-combustible nature ensures that it maintains its integrity under heat stress, providing long-term protection with minimal degradation.
Fiberglass is relatively durable but can become brittle and degrade over time when exposed to constant temperature fluctuations or extreme heat, leading to reduced performance.
Mineral Wool is generally durable but is more susceptible to damage from moisture and physical impact. Over time, it can lose its insulating properties if exposed to wet conditions.
Ceramic fiber blankets stand out for their ability to maintain thermal efficiency in challenging conditions, reducing the need for frequent replacement or repair.
3. Lightweight Design: Easy Handling and Installation
One of the key advantages of ceramic fiber blankets is their lightweight design, which makes them easy to handle and install, even in large or complex industrial setups. This provides both operational and cost benefits, including:
Ceramic Fiber Blanket is notably lighter than both fiberglass and mineral wool, making it easier to cut, shape, and install. Its flexibility allows it to fit into tight spaces and around irregular shapes, offering superior versatility.
Fiberglass is also lightweight, but its flexibility and ease of installation are not on par with ceramic fiber, especially when working with large surfaces or intricate designs.
Mineral Wool tends to be heavier and less flexible, which can make installation more difficult, especially in high-temperature applications where ease of handling is critical.
The lightweight nature of ceramic fiber blankets reduces labor costs and installation time, making it a more efficient option for many industrial applications.
4. Cost-Effectiveness: Balancing Price and Performance
When evaluating insulation materials, cost-effectiveness is always a major consideration. While ceramic fiber blankets offer superior heat resistance and durability, their initial cost is typically higher than that of fiberglass or mineral wool. However, over time, ceramic fiber blankets can provide significant cost savings due to their longer lifespan and enhanced thermal performance.
Fiberglass is often the most affordable insulation material, making it an attractive choice for lower temperature applications. However, its shorter lifespan and reduced performance at higher temperatures may lead to higher long-term costs, as it may need to be replaced more frequently.
Mineral Wool typically falls between fiberglass and ceramic fiber in terms of cost. While it offers better heat resistance than fiberglass, it doesn’t match ceramic fiber in terms of thermal efficiency or durability.
Although ceramic fiber blankets may have a higher upfront cost, they offer better long-term value, especially in applications where high heat retention and minimal maintenance are critical.
5. Versatility and Application Range
Ceramic fiber blankets, fiberglass, and mineral wool all offer varying degrees of versatility in terms of application. However, ceramic fiber blankets excel in high-temperature settings:
Ceramic Fiber Blanket is highly versatile and can be used in a variety of high-temperature applications, including furnace linings, fireproofing, exhaust systems, and heat shields. Their flexibility allows them to be used in both residential and industrial settings.
Fiberglass is commonly used for insulation in lower-temperature environments, such as HVAC systems, and as pipe insulation in some cases. However, its use is limited in very high-temperature applications.
Mineral Wool is often used in industrial settings as a thermal insulator, particularly in applications where moisture resistance is necessary, such as in pipes and tanks. However, it doesn’t provide the same level of heat retention as ceramic fiber in extremely high-heat environments.