#Industry News
An introduction to OLED displays
OLED displays have transformed the visual technology landscape with their exceptional image quality, flexibility, and energy efficiency.
I. An introduction to OLED displays
In recent years, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays have emerged as a revolutionary technology in the field of visual displays.
Offering vibrant colors, deep blacks, and energy efficiency, OLED displays have gained popularity in various consumer electronics.
II. Structure of OLED
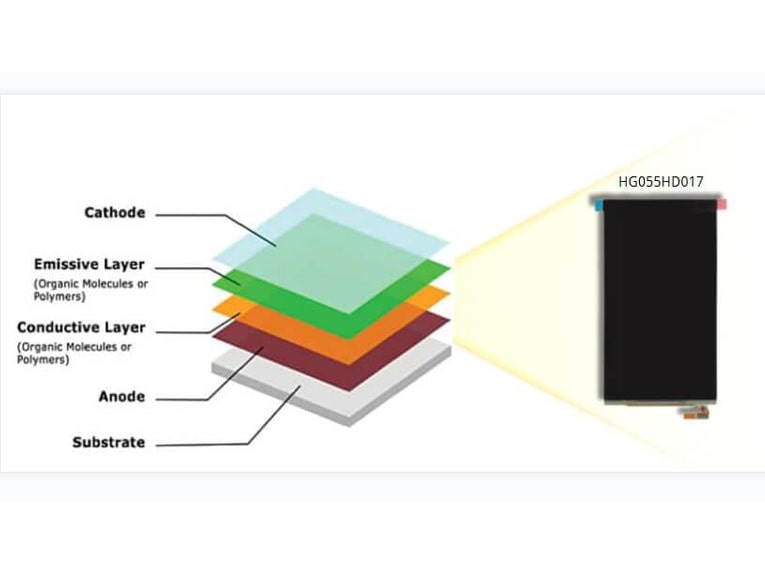
The structure of an OLED display can be divided into several key components, each playing a vital role in the functioning of the display. Let’s explore the structure of an OLED display:
● Substrate: The substrate is the base layer of the display, typically made of glass or transparent plastic. It provides structural support and acts as a foundation for other layers.
● Anode: The anode, usually made of transparent conductive material like indium tin oxide (ITO), is placed on the substrate. It serves as the positive electrode and carries the electrical current into the OLED structure.
● Organic Layers: The organic layers are the heart of the OLED display. They consist of multiple sublayers, each with a specific function:
- Hole Transport Layer (HTL): The HTL facilitates the movement of positively charged “holes” from the anode.
- Emissive Layer: This layer contains organic molecules that emit light when an electric current passes through. Different organic materials can be used to achieve different colors.
- Electron Transport Layer (ETL): The ETL assists in transporting negatively charged electrons from the cathode.
● Cathode: The cathode is the negative electrode of the OLED display. It is typically made of a low-work function metal or alloy, such as aluminum or calcium. The cathode injects electrons into the OLED structure.
● Encapsulation: To protect the organic layers from moisture and oxygen, an encapsulation layer is applied on top of the OLED structure. It helps to extend the lifespan of the OLED display.
III. Working Principle of OLED
When an electric current is applied to the OLED structure, it causes a flow of electrons from the cathode and positively charged holes from the anode.
The electrons and holes meet and combine in the emissive layer, releasing energy in the form of light. The organic materials used in the emissive layer determine the color of light emitted. As there is no need for a separate backlight, each pixel can be individually controlled, allowing for precise brightness and color representation.
IV. Advantages of OLED
OLED displays offer several advantages over conventional LCD display technologies. Firstly, they deliver superior image quality, with vibrant and accurate colors, wider viewing angles, and faster response times.
Secondly, OLED displays are incredibly thin and flexible, making them suitable for curved and foldable devices. Additionally, OLED technology enables power-efficient displays, as it does not require a separate backlight and only consumes energy for activated pixels.
Related:What is a TFT LCD?
V. Applications of OLED
OLED displays have found their way into a wide range of devices across industries. In smartphones, OLED screens provide immersive visual experiences and enable features like always-on displays and in-display fingerprint sensors.
OLED technology has also revolutionized the television industry, with ultra-thin and high-resolution OLED TVs offering breathtaking picture quality. In the automotive sector, OLED displays are being integrated into dashboards, infotainment systems, and rear-view mirrors, enhancing safety and aesthetics.
Furthermore, OLED displays have made significant contributions to the wearable technology market, where they are used in smartwatches, fitness trackers, and augmented reality (AR) glasses. In the healthcare domain, OLED displays are utilized in medical devices, such as patient monitors and diagnostic equipment, due to their high contrast and accuracy.
VI. Conclusion
OLED displays have transformed the visual technology landscape with their exceptional image quality, flexibility, and energy efficiency.
As the demand for more immersive and visually appealing displays continues to grow, OLED technology is poised to play a vital role in various industries, ranging from consumer electronics to automotive and healthcare.
With ongoing advancements, OLED displays are expected to become even more versatile, delivering groundbreaking innovations in the future. Embracing the potential of OLED technology opens up a world of possibilities, offering an exciting future for visual experiences.