#White Papers
5 Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Technologies
There are 5 TFT technologies used in LCD and OLED, a-Si, IGZO, LTPS, CGS, and HTPS. a-Si is the most common material due to its low cost and mature technology, while LTPS has much improvement in electron mobility.
Thin-film-transistor technology used in the display industry has contributed to significant improvements in the display qualities such as addressability, contrast, and fast response.
The fabrication of TFT is to use the technology of microelectronics fine processing on silicon (Si), and transplant it to the processing of TFT array on large-area glass.
The application of TFT technology has developed from actively driving TFT LCD to OLED, and even in electronic paper.
I. Classification of TFT technology by material
The active material of TFT is the silicon film.
In light of the structure and technology of silicon film, the TFT substrate can be divided into amorphous silicon (a-Si), indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO), low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS), high-temperature polysilicon (HTPS), continuous granular crystalline silicon (CG Silicon).
Currently, a-Si, IGZO, and LTPS LCD are the most common TFT materials in the market.
- a-Si (Amorphous Silicon)
a-Si is the non-crystalline form of silicon.
At present, a-Si is the most popular option in the LCD industry for its simple technology and low cost.
Advantages
• Low cost
• Simple and mature technology
Disadvantages
• Low aperture ratio: the switch occupies a large area of the pixel. It causes difficulty in enhancing the brightness of the display
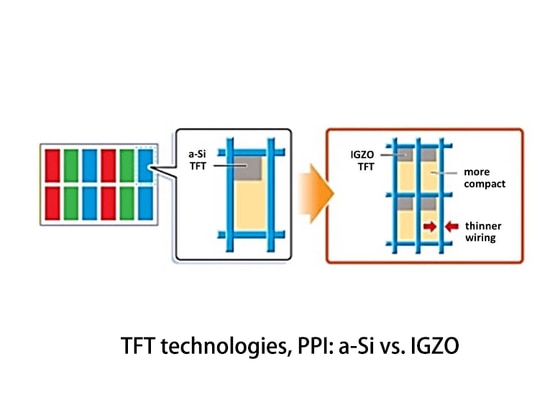
• The PPI is also limited to the level of about 200 PPI
Given its advantage, it is suitable for large-size LCDs and inexpensive EPD (electrophoretic display) panels at present.
- IGZO (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide)
Amorphous IGZO material is a channel layer material used in the new generation TFT technology and is one kind of metal oxide panel technology.
Advantages
• High electron mobility
• Good uniformity
• Transparency
• Simple manufacturing process
• Compared with a-Si, it has much better bending properties and can be used for flexible display
Disadvantages
• Relatively short lifespan
• Since it is sensitive to water, light, and oxygen, the reliability and stability of the operation will decline to a certain extent after the long-running. In production, it needs an additional protective layer as compensation means which increases the barrier and cost in mass production
Given the PPI of IGZO TFT can reach about 300, it is popular adoption in consumer goods and large-size monitors.
- LTPS (Low Temperature Poly-silicon)
LTPS is formed after being uniformly irradiated with laser light, the a-Si absorbs internal atoms to undergo energy level transitions and transform into a polycrystalline structure.
LTPS technology is a perfect match with OLED. The molecular structure of polysilicon is arranged neatly and directionally in grain, so the electron mobility is 200-300 times faster than that of disordered amorphous silicon.
Advantages (vs. a-Si and IGZO)
• Higher electron mobility
• Higher resolution
• Faster reflection speed
• Higher brightness
• Perfectly matched with OLED
• The PPI can reach up to 500+
Disadvantages
• Relative high cost
Hence, LTPS is the suitable option for small-and-medium-sized high-end LCD panels with higher requirements for resolution (PPI above 300) and electron mobility.
- CGS (Continuous Grain Silicon)
CGS is a variant of LTPS, belonging to the paten of Sharp.
Advantages
• Its carrier mobility speed is 3 times faster than LTPS technology and 600 times than normal a-Si technology
• Higher aperture ratio: the same brightness of the backlight can produce higher brightness of the display and vice versa.
• Energy saving
• Thinner
• More resistant to impact and distortion
Disadvantages
• Low yield
• High cost
- HTPS (High Temperature Poly-Silicon)
HTPS is used in a transmissive LCD with an active matrix drive method.
Each pixel has thin-film transistors made of polysilicon, and these pixel transistors switch conduction/non-conduction by changing the voltage of the scanning line and playing the role of a switch.
Advantages
• Small size
• High precision and contrast
• Multi pixel
• High aperture ratio
• Built-in driver
Disadvantages
Even though HTPS is one of the TFT technology, it cannot be directly used for mobile phones or computer screens due to the screen of them are direct-view screens.
It is usually used in amplified display products, such as LCD projectors, rear projection TV, etc.
II. Comparison of 3 common TFT technologies: a-Si, IGZO, and LTPS
In general, in comparison, the LTPS panel has the most advanced technology and the best display effect, but the only disadvantage is the low yield rate and high cost. In contrast, a-Si, the lowest cost, is the most widely used, followed by high-end LTPS.
It can be simply seen that IGZO is a technology between a-Si and LTPS. Its advantage is to achieve a balance between effect and cost. The display effect is close to that of LTPS panels, and the cost is closer to a-Si.
However, IGZO has technical authorization problems, and there are certain restrictions on use and mass production.
Since LTPS is too expensive to use on large screens, IGZO is used instead to appear on large-screen devices such as tablets.
Recap above pros and cons of the above three common TFT technologies:
If you want to know more about the display technology applicable to your project, please do not hesitate to contact our engineering team for more discussion.