#White Papers
Raman Spectroscopy Of Pigmented Human Tissue In The Shortwave Infrared
Low-Noise InGaAs Camera to Accelerate Melanoma Diagnosis
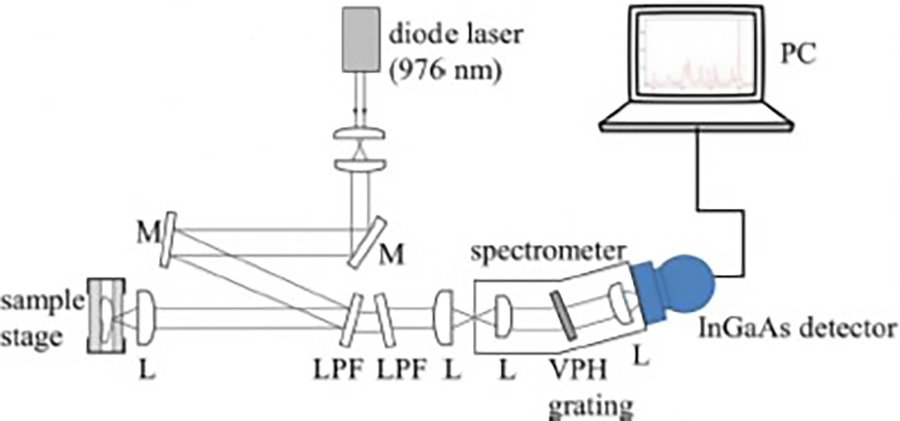
Researchers at the Erasmus MC University Medical Center and at RiverD International B.V., Rotterdam, the Netherlands, have developed a novel, cutting-edge method of applying shortwave-infrared Raman spectroscopy at a wavelength above 1 µm to the examination of darkly pigmented human tissue, thereby greatly subduing the spectral disturbances by fluorescence effects in the visible realm. This will substantially further and accelerate the diagnosis of melanoma. Key to this unique achievement is an image capture technology developed by Xenics, based in Leuven, Belgium. Their LN2-cooled Cougar-640 camera features an extremely low-noise (<20e- typically) InGaAs area array detector with 640 x 512 pixels and a special nondestructive readout scheme called “Read While Integrate.”


