#Product Trends
What are Gantry Robots?
Types and Applications of Multi-axis Linear Motion System.
Types of Robot Gantry
Robot gantries come in various shapes and sizes, and each type is designed to perform specific tasks. Here are the main types of robot gantry:
Cartesian Gantry
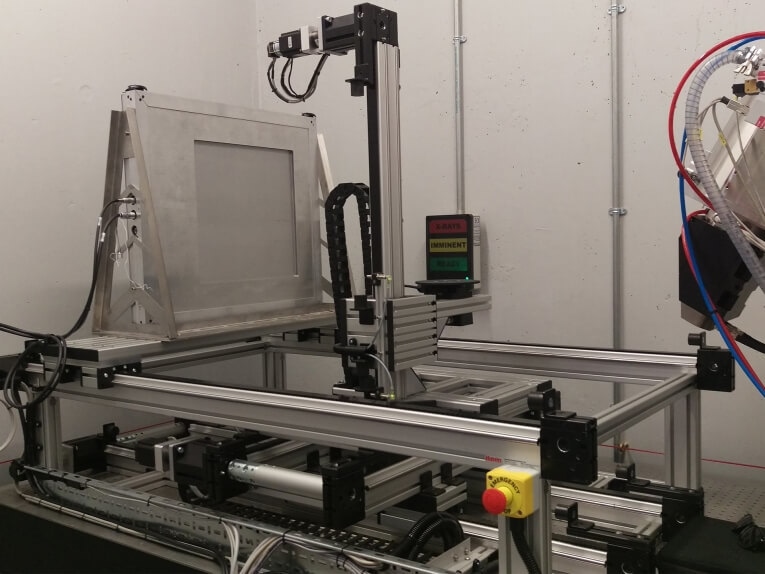
Cartesian gantries, also known as linear robot gantries, are the most commonly used type of robot gantry. They consist of two or more linear axes that move in a straight line along the X, Y, and Z axes. The robot arm is mounted on a carriage that moves along the gantry structure, allowing it to reach different points within the work envelope.
Cartesian gantries are known for their high accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for applications that require precise positioning. They are often used in Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining, 3D printing, and pick-and-place operations.
Articulated Gantry
Articulated gantries consist of multiple segments that are connected by joints or links. Each joint can rotate around its axis, giving the robot a greater degree of freedom and flexibility than a Cartesian robot gantry. Articulated gantries are commonly used in applications that require a high level of dexterity, such as pick-and-place applications, welding, and painting.
Articulated gantries can reach any point within their workspace by bending their joints, and they are often used in applications that require complex movements. They are also used in collaborative robots or cobots that can work safely alongside human operators.
Parallel Gantry
Parallel gantries, also known as parallel manipulators or delta robots, consist of a series of parallel links that are connected to a fixed base and a moving platform. The robot arm is mounted on the moving platform, and the links are driven by a series of actuators that control the movement of the platform. Parallel gantries are known for their high payload capacity and stiffness, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as material handling and assembly. They are often used in the food and beverage industry for packaging and palletizing operations, where speed and accuracy are critical.
Hybrid Gantry
Hybrid gantries combine the features of two or more gantry system configurations to create a customized solution for specific applications. For example, a hybrid gantry may combine the high accuracy of a cartesian gantry with the flexibility of an articulated gantry, or the high payload capacity of a parallel gantry with the precision of a Cartesian gantry.
Hybrid gantries are often used in applications that require a unique combination of features that cannot be achieved with a single gantry type.
Each type of robot gantry has its unique features and benefits, depending on the application requirements. Cartesian gantries are known for their high accuracy and repeatability, while articulated gantries are more flexible and can work in confined spaces. Parallel gantries have a high payload capacity and stiffness, while hybrid gantries offer a customized solution for specific applications.
When selecting a robot gantry, it’s essential to consider the specific application requirements to determine which type of gantry is best suited for the task. Factors such as the size and weight of the parts, the speed and accuracy of the operation, and the workspace limitations must be taken into account.
Applications of Robot Gantry
Robot gantries are widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and logistics, where precise and repetitive movements are required. Here are some typical applications of robot gantries:
Material Handling
Robot gantries are widely used in material handling applications, where they can move heavy and bulky materials with high precision and speed. Material handling applications include palletizing, depalletizing, and loading and unloading of products.
In a palletizing application, the robot gantry can pick up boxes or products from a conveyor and place them onto a pallet in a specific pattern. In a depalletizing application, the robot gantry can pick up and place products from a pallet onto a conveyor.
Welding
Robot gantries are widely used in welding applications, where they can perform repetitive welding tasks with high precision and accuracy. Welding applications include spot welding, arc welding, and laser welding.
In a spot welding application, the robot gantry can pick up a welding gun and perform spot welds on a workpiece in a specific pattern. In an arc welding application, the robot gantry can pick up a welding torch and perform welds on a workpiece while moving along a specific path. In a laser welding application, the robot gantry can pick up a laser and perform welds on a workpiece with high precision.
Painting
Robot gantries are widely used in painting applications, where they can paint complex shapes and surfaces. Painting applications include automotive painting, aircraft painting, and industrial painting.
In an automotive painting application, the robot gantry can pick up a spray gun and apply paint to a car body while moving along a specific path. In an aircraft painting application, the robot gantry can pick up a spray gun and apply paint to an aircraft body. The robot gantry can pick up a spray gun and apply paint to large parts or structures in an industrial painting application.
Inspection and Testing
Robot gantries are widely used in inspection and testing applications, where they can perform accurate and repetitive measurements and tests. Inspection and testing applications include quality control, non-destructive testing, and metrology.
In a quality control application, the robot gantry can pick up a sensor and perform measurements on a workpiece to ensure it meets the required specifications. In a non-destructive testing application, the robot gantry can pick up a sensor and perform tests on a workpiece to detect any defects or flaws. In a metrology application, the robot gantry can pick up a sensor and perform precise measurements on a workpiece to determine its dimensions and tolerances.