#Product Trends
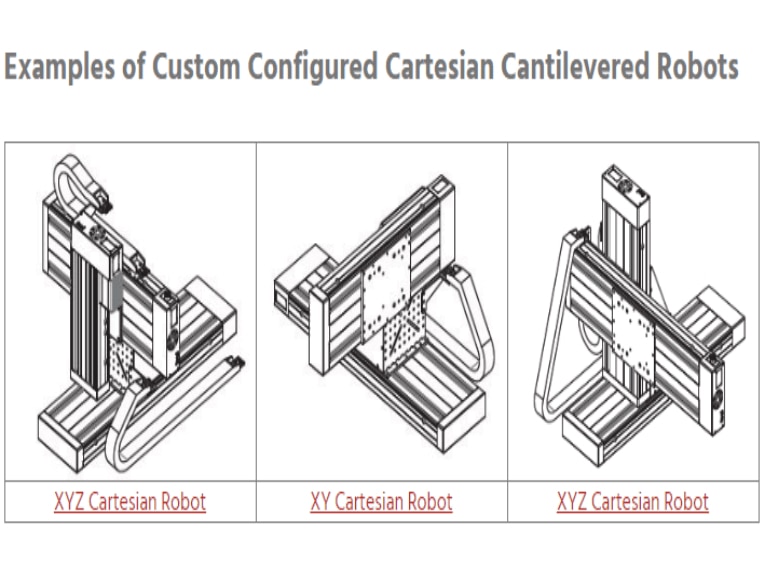
What is a Gantry or Cartesian Robot?
Common gantry robot applications.
Gantry robots are boxy robotic arms that move linearly along a fixed overhead track. They’re ideal for precision applications like pick and place, loading and unloading parts, and assembly tasks that need high accuracy and repeatability over a large area.
Simple, precise and powerful: Gantry robots have a simple but robust design. They typically have three axes of motion – X, Y, and Z. The X and Y axes allow horizontal movement along the overhead track, while the Z axis controls the vertical motion. This simplified motion and fixed base give Gantry robots super-high precision and repeatability.
Cost-effective for large-scale operations: Due to their streamlined design and the ability to cover large areas without the need for multiple units, gantry robots reduce the cost per unit of production, especially in large-scale manufacturing environments.
Versatile across various industries: Their adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive assembly lines to complex 3D printing, showcasing their versatility across different sectors.
Minimal maintenance necessary: Gantry robots, with their straightforward design and fewer moving parts compared to articulated robots, often require less maintenance, leading to lower downtime and higher productivity.
How does a gantry robot work?
Now you have the lowdown on what a gantry robot is. But how do they operate, exactly, and what makes them so special?
A look at their features will clear that up real quick:
1. Going linear: In gantry bots, two beams are attached perpendicularly to form a bridge-like structure; the beams move independently along tracks or guides, powered by motors and drive mechanisms. This allows the robot to position itself anywhere within its range.
2. Complex task execution: At the end of the robotic arm, various tools or end-effectors can be attached based on the specific task at hand — be it picking, placing, assembling, or welding. The robot’s controller, which is a sophisticated computer system, dictates the movements of the arm and the operation of the end-effector.
3. Programmable path: Gantry robots are programmed to follow precise paths and (very) repeatable motions. Complex software controls the robot’s movement and provides instructions for its tasks. The robot can store many programmed paths and positions for quick access when needed.
4. Multi-axis motion: Multiple axes give the robot flexibility to manipulate objects in different orientations.
5. Precise positioning: Gantry robots offer an extremely high degree of accuracy and repeatability. They can position objects within 0.1 millimeters, allowing them to perform high-precision assembly, packaging, and manufacturing operations. Feedback devices help make sure the robot maintains the correct position and path.
What are gantry robots good at?
Where is the sweet spot with gantry robots? In highly repetitive tasks that require precision and consistency. Their rigid structures and programmable nature mean they can accurately perform the same motions over and over — and pretty much forever.
This results in:
1. Through-the-roof throughput: Gantry robots are a match made in heaven for high-volume production environments. They can work tirelessly with zero breaks and zero complaints.
2. This means that, in a factory setting, gantry robots are often used in applications like palletizing, packaging, and machine loading/unloading that require handling hundreds or even thousands of items per hour.
3. Heavy-duty lifting: Gantry robots can also handle very heavy payloads, up to several tons. Their fixed base and rigid structure are designed to support substantial weight without compromising performance. This makes them well-suited for demanding applications like high-grade palletizing, packaging, and machine tending.
4. Very large work envelopes: The overhead track provides gantry robots with a huge work envelope, often covering an entire warehouse or factory floor. This allows them to service multiple workstations or access hard-to-reach areas. Basically, the only limitation to their work envelope is the size of the track.
What are the most common gantry robot applications?
Gantry robots are already very widely used across many industries.
Some of the most popular use cases are:
1. Palletizing: Refers to the process of stacking boxes, bags, or other units onto pallets. Gantry robots are marvelous at palletizing because their linear motion allows them to pick up items and place them accurately on pallets. Their large work envelopes mean they can handle pallets of many sizes.
2. Machine Loading/Unloading: Gantry robots are ideal for loading and unloading parts or materials into and out of other machines like CNC machines, ovens, or conveyor belts. Their precise motion control and ability to handle heavy loads make them perfect for automating these repetitive, super-boring tasks.
3. Packaging: Gantry robots are very frequently used in packaging operations like case packing, cartoning, and shrink wrapping. Their linear motion is excellent for manipulating boxes and other packaging over a wide area. Gantry robots can pick up, move, and zoom by at dizzyingly fast speeds — without losing any accuracy.
4. Storage and retrieval: Gantry robots are commonly used in automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) in warehouses and distribution centers. Because they can travel large distances and lift heavy materials, they can store and retrieve pallets, crates, or racks in high-rise storage structures. All in all, Gantry robots help maximize storage density and improve efficiency in these facilities.