#White Papers
You can control ESD by humidification system
The presence of moisture prevents static electricity from accumulating on surfaces, causing it to disperse into the atmosphere instead.
Preventing static electricity(ESD) in industrial environments is crucial, and creating an environment where static electricity does not occur is the best approach. The bathroom serves as an example of such an environment, as it remains free from static electricity due to its high humidity. The presence of moisture prevents static electricity from accumulating on surfaces, causing it to disperse into the atmosphere instead.
Two measures are used to quantify humidity: relative humidity (RH) and absolute humidity. While it is generally recommended to maintain a relative humidity of 50% or higher to combat static electricity, the absolute humidity, which depends on temperature, plays a significant role. Even at the same relative humidity, the amount of water present in the air (absolute humidity) varies greatly with temperature.
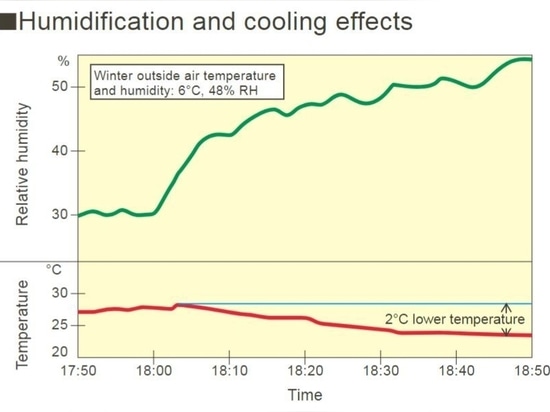
To effectively counter static electricity, humidification is a valuable method, particularly during winter when dry air promotes static buildup. Various humidification methods can be employed, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Choosing the appropriate method depends on the specific requirements of the production site. Methods such as the belows.
1. humidifying with steam (using boilers, electrodes, or electric heating)
2. humidification by evaporation (utilizing drop permeation or wet membrane types)
3. humidification by water mist (using spray or ultrasonic types)
Let's check the characteristics of each humidification method will be examined in detail to identify the most suitable approach for specific production your sites.