#Industry News
How to Measure the Porosity of Nanofibers
Porosity of Nanofibers
Nanofibers possess a range of unique properties that make them important components in applications such as energy storage, filtration, sensors, and tissue engineering. They are small in diameter, 10 to 100 nanometers, have a high surface area and porosity and are manufactured from organic and inorganic polymers via various techniques. Nanofibers significantly impact multiple industries, but their unique properties are often influenced by their porosity, thus making it an important aspect to measure. Therefore, in this blog post, we explain what methods are used to measure nanofiber porosity and the benefits of doing so.
Measuring Nanofiber Porosity
There have been many challenges to date in measuring nanofiber porosity, including limited control over testing parameters and using unsuitable solvents, which negatively affect the samples. However, it is a crucial process as measuring and adapting porosity is required to produce optimal nanofiber properties for specific applications such as high-performance filters, drug manufacturing, and more1. To overcome prior disadvantages, several testing methods have been developed to offer effective measuring of nanofiber porosity, such as gas expansion, fluid displacement, and image analysis.
Gas Expansion
The gas expansion method is based on the Boyle-Marriote Gas Law and can be used to measure nanofiber porosity in a quick and effective manner. The process involves placing a sample in a chamber, then allowing gas to enter the chamber, which fills the pores in the nanofibers. The results are obtained by measuring the gas volume entering the chamber and the expansion and accompanying fall in pressure.2 This method is suitable for analyzing porous materials of all shapes and sizes and is widely used in laboratories for measuring porosity.
Fluid Displacement
Fluid or liquid displacement is another popular method for measuring the porosity of materials. This technique is conducted by submerging a sample, such as nanofibers, in a liquid and measuring the volume of liquid that is displaced by the sample. The porosity of the nanofibers, or other materials, is determined by measuring the difference between the volume of the sample and the volume of the displaced liquid.3 This is another simple method that does not require expert training but does run the risk of damaging the sample during the immersion process.
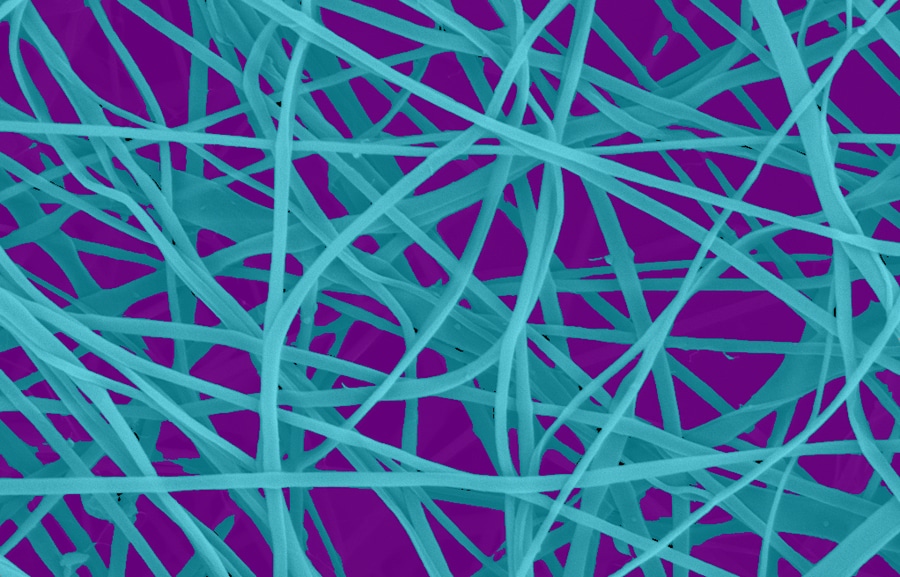
Image Analysis
Image analysis is quickly becoming a favored method of determining material porosity. It involves using a microscope or another imaging instrument to capture images of the nanofibers, which can then be analyzed. The captured images will allow scientists to determine the pore size, shape, and distribution, which can be used to calculate the overall porosity. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a non-destructive technique that is used for measuring porosity on a range of materials, including nanofibers.
MIPAR and Measuring Porosity
MIPAR is a world-leading image analysis software company that specializes in accurately and reliably obtaining measurements from complex images. Our products support researchers and scientists in a wide range of industries, from aerospace to life sciences, and benefits customers around the world.
As mentioned above, image analysis is a favorable method of measuring porosity. For applications that require measuring nanofiber porosity and thickness, MIPAR offers world-class imaging software created by industry experts. Contact us today to learn more about measuring nanofiber porosity.
References and Further Reading
1. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0921510717300016
2. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/155892501300800408
3. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0376738897000173





