#Industry News
Hot Air Furnace
Introduction and Classification of Hot Air Furnace
What is a Hot Air Furnace?
The hot air furnace is a thermodynamic machine. It was widely used in China in the late 1970s. It has become a replacement product of electric heat sources and traditional steam power heat sources in many industries. There are many types and complete series of hot air furnaces, which are divided into manual firing type and mechanical firing type in terms of coal adding method , coal furnace, oil furnace and gas furnace in terms of fuel type, high temperature furnace and medium temperature furnace in terms of output air temperature, indirect type and direct type in terms of conveying form, combined type and separate type in terms of arrangement form of heat exchanger. Coal pulverizer is equipped on large furnace.
Classification of Hot Air Furnace
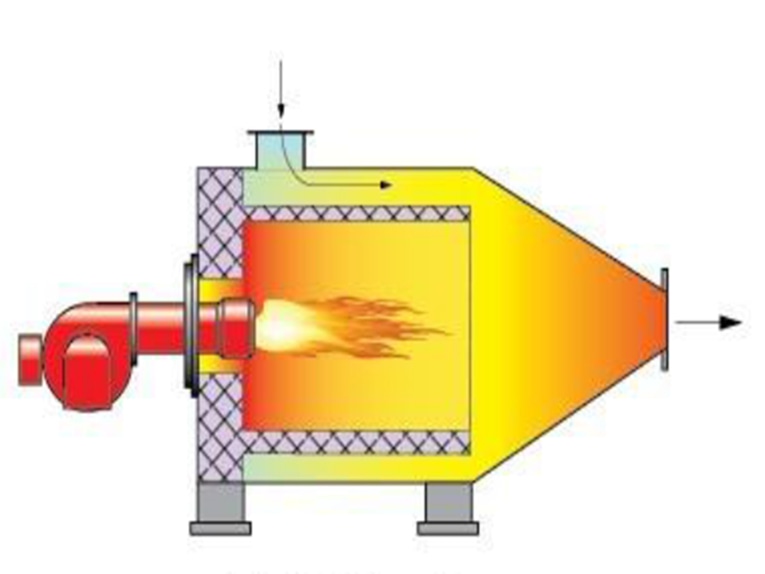
1. Direct high purification hot air furnace
It adopts direct combustion of fuel, forms hot air through high purification treatment, and directly contacts with the material for heating, drying or baking. The fuel consumption of this method is about half that of steam or other indirect heaters. Therefore, the direct high-purity hot air can be used without affecting the quality of the dried product.
Fuels can be divided into the following categories:
(1)Solid fuel, such as coal and coke.
(2)Liquid fuel, such as diesel, heavy oil, alcohol-based fuel.
(3)Gas fuel, such as coal gas, natural gas, liquid gas.
After reaching a certain temperature, it directly enters the drying chamber or baking chamber, contacts with the material to be dried, heats and evaporates the water to obtain dried product. In order to utilize the combustion reaction heat of these fuels, a set of fuel combustion devices must be added. Such as: coal burners, oil burners, gas burners, etc.
2. Indirect high purification hot air furnace
Indirect hot air furnace: It is mainly suitable for drying materials that are not allowed to be contaminated, or for drying heat-sensitive materials with lower temperature. For example: milk powder, pharmaceuticals, synthetic resins, fine chemicals, etc. This type of heating device uses steam, thermal oil, flue gas, etc. as a carrier to heat air through various forms of heat exchangers.
The essential problem of indirect hot air furnace is heat exchange. The larger the heat exchange area, the higher the heat conversion rate, the better the energy saving effect of the hot air furnace, and the longer the life of the furnace body and heat exchanger. Conversely, the size of the heat exchange area can also be identified from the flue gas temperature. The lower the flue gas temperature and the higher the heat conversion rate, the larger the heat exchange area.
After the separation of fuel and heating source, it can be used for human heating. The working principle can be divided into two types: regenerative type and heat exchange type.
3. Regenerative type furnace
According to the heat storage body inside the hot air furnace, there are a ball type hot air furnace (referred to as a ball furnace) and a hot air furnace using checker bricks. According to the combustion method, it can be divided into top combustion type, internal combustion type, and external combustion type. How to increase the air temperature is the direction of long-term research in the industry. Common methods are to mix high calorific value gas, or increase the heat exchange area of the checker bricks of the hot air furnace, or change the material and density of the checkers brick, or change the shape of the heat storage body (such as heat storage ball), and use various methods to preheat the gas and combustion air.
Advantages: high heat exchange temperature and high heat efficiency.
Disadvantages: large size, large floor area, unstable hot air temperature, overmany switching mechanisms, easy to cause problems, short heat storage body life, high maintenance cost, and extremely high purchase cost.
4. Heat exchange type furnace
It mainly uses the high-temperature heat exchanger as the core component, which can not use metal heat exchangers, only high-temperature-resistant ceramic heat exchangers can be used. The gas is fully burned in the combustion chamber. The hot air after combustion passes through the heat exchanger and exchanges heat with fresh cold air, which can make the fresh air temperature reach above 1000℃.
Advantages: high heat exchange temperature, high heat efficiency, small volume, stable hot air temperature, no switching mechanism, long life, low maintenance cost, low purchase cost.
Disadvantages: The heat exchange temperature is not as high as the regenerative type. It appears later, and is not widely used.





