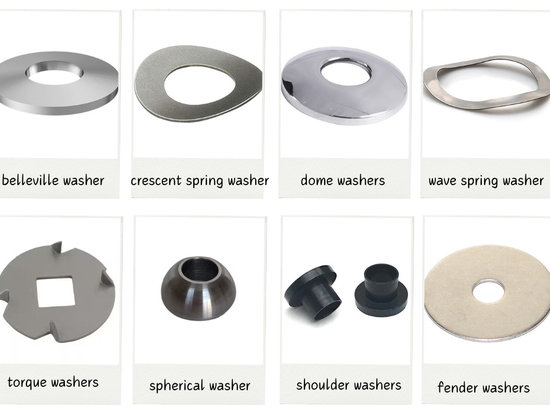
#Industry News
What Is Zinc Die Casting
Definition And Advantages
Zinc die casting utilizes a zinc alloy as its primary raw material, typically comprised of a blend of zinc, aluminum, copper, magnesium, and other alloys, commonly referred to as Zamak alloy.
The process involves a rapid-cycle hot chamber die casting method, wherein a gooseneck component is submerged within a furnace filled with molten metal. The molten metal automatically flows into the injection chamber through the gooseneck orifice. Subsequently, a vertical plunger seals the orifice and applies high pressure to propel the molten metal into the rear of the mold. The part solidifies swiftly, typically within seconds, before being ejected from the tool.
Zinc alloy holds a distinctive position among die-casting materials due to several factors. Similar to aluminum, zinc offers commendable strength, rigidity, and resistance to corrosion. Additionally, zinc die castings boast unique advantages over other metal die castings.
Zinc alloys feature lower melting points and superior fluidity, enabling them to efficiently fill intricate mold cavities during the die-casting process, resulting in parts with complex geometries.
With high precision and minimal shrinkage, zinc die castings often exhibit enhanced dimensional stability and accuracy, yielding more precise components. Typically, the size of zinc alloy castings can achieve tolerances ranging from IT11 to IT13, and occasionally even as tight as IT9.
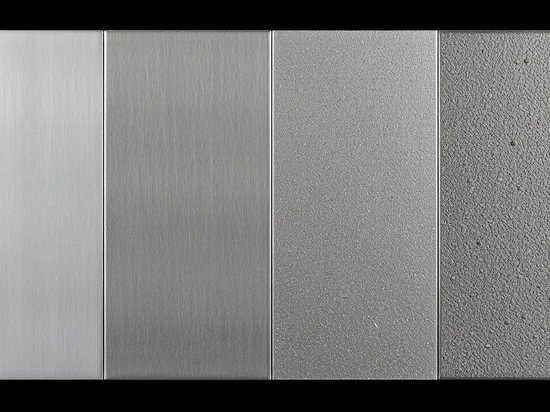
Zinc die casting meets stringent aesthetic demands, with various surface treatment processes such as spraying, anodizing, etc., capable of achieving diverse appearance effects. The surface roughness of zinc alloy die castings ranges from Ra0.8 to 3.2μm, occasionally even as low as Ra0.4μm.
Compared to other metal materials, zinc alloy offers lower raw material costs. Moreover, zinc die casting is an efficient production process capable of rapidly manufacturing large quantities of parts, thereby reducing overall production expenses.