#Industry News
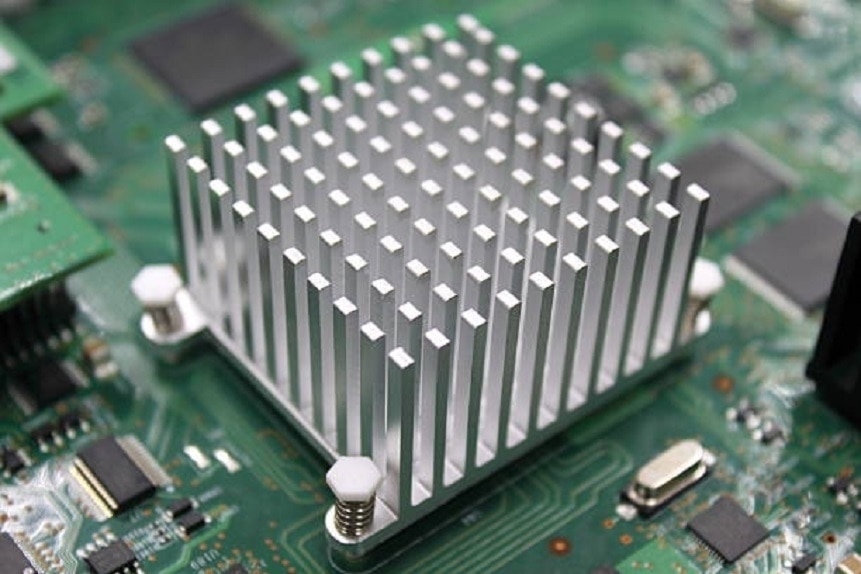
What Is A Heat Sink ?
How Does A Heat Sink Work?
A heat sink serves as a vital component in electronic systems, facilitating the efficient dissipation of heat generated during operation. Constructed typically with a base and fins, heat sinks leverage principles of conduction, convection, and sometimes radiation to transfer heat away from heat-producing devices or sources into the surrounding environment or a heat transfer fluid.
As electronic devices, such as electronic components or mechanical parts, operate, they inevitably generate heat. The heat sink, in direct physical contact with these components, absorbs this heat. Its extended surface area, often comprising fins, enhances heat dissipation by facilitating air flow. As air flows over the fins, it carries away the absorbed heat, gradually cooling the heat sink.
The warming of the surrounding air by the heat sink creates a natural upward flow, drawing in cooler air from the surroundings. This natural convection process aids in further dissipating heat away from the heat sink, maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
In scenarios where natural convection proves inadequate, forced convection mechanisms come into play. Fans or blowers actively move air across the heat sink's surface, significantly enhancing heat transfer and accelerating cooling. This forced convection ensures efficient heat removal, crucial for sustaining the performance and longevity of electronic systems.