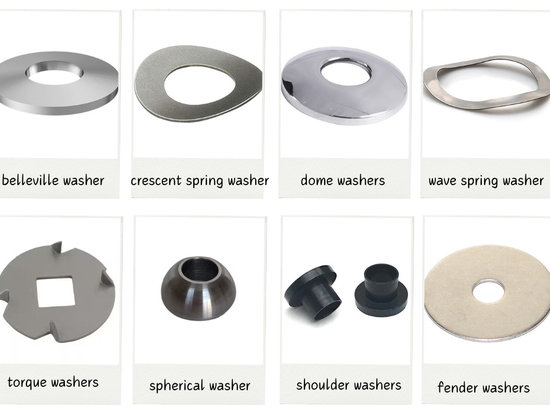
#Industry News
Common Types Of Metal Casting Defects
What You Need To Know
The majority of casting defects fall into six main categories: gas porosity, shrinkage defects, metallurgical issues, problems with pouring metal, mold material flaws, and shape imperfections.
1.Gas Porosity: Gas porosity defects occur when gas is trapped within the casting during solidification, resulting in voids or bubbles in the metal. These defects can weaken the casting and affect its integrity.
2.Porosity Defects: Porosity defects refer to the presence of voids or pores in the casting material. These voids can be caused by gas entrapment, shrinkage, or incomplete fusion of the molten metal during solidification.
3.Shrinkage Defects: Shrinkage defects occur due to insufficient molten metal to fill the entire mold cavity during casting, leading to voids or cavities in the casting upon solidification. There are two main types:
4.Open Shrinkage Defects: These occur on the surface of the casting and are visible to the naked eye.
5.Closed Shrinkage Defects: These defects are internal and not immediately visible, often requiring non-destructive testing for detection.
6.Warping: Warping defects refer to the distortion or bending of the casting due to uneven cooling or improper mold design. This can result in dimensional inaccuracies and affect the functionality of the final product.
7.Metallurgical Defects: Metallurgical defects include various flaws in the metal structure of the casting, which can affect its mechanical properties. Examples include hot tears, cold shuts, and slag inclusions.
8.Hot Tears: Hot tears are cracks that develop in the casting during solidification due to internal stresses caused by uneven cooling or insufficient ductility of the metal.
9.Cold Shuts: Cold shuts occur when two streams of molten metal fail to fuse properly during casting, resulting in a visible seam or line in the casting.
10.Slag Inclusions: Slag inclusions are non-metallic impurities, such as oxides or flux, trapped within the casting during pouring. These inclusions can weaken the casting and reduce its integrity.
11.Pouring Metal Defects: Pouring metal defects include issues related to the pouring process itself, such as sinks (depressions on the casting surface), dross (oxidized metal on the surface), and other surface imperfections.
12.Mold Material Defects: Mold material defects arise from issues with the mold material itself, such as fusion (fusion of mold material with the casting), cuts and washes (erosion of mold material), and drops (fragments of mold material breaking off).
13.Casting Shape Defects: Casting shape defects refer to discrepancies between the intended and actual shape of the casting, such as mismatches in dimensions or features.
These common casting defects can be caused by a variety of factors, including improper casting parameters, improper mold design, and material impurities. Identifying and addressing these defects is critical to producing high-quality castings with the desired properties and dimensions. If you want more details, please click on the link below. This article combines die casting defects with easy-to-understand everyday behaviors such as baking, cooking, etc.