#Industry News
Exploring 15 Different Types of Casting Processes
2024
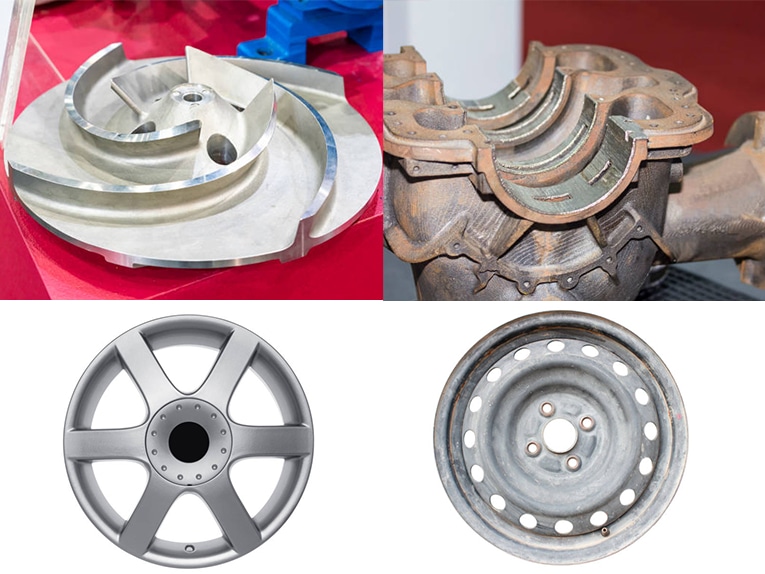
Casting is a vital manufacturing process used to create intricate metal parts and components for various industries. From automotive to aerospace, casting techniques play a crucial role in producing high-quality parts efficiently. Let's delve into 15 different types of casting processes and understand their unique characteristics and applications.
1. Metal Die Casting:
Utilizes reusable metal molds to produce complex, high-precision parts with excellent surface finish. Widely used in automotive and consumer electronics industries.
2. Sand Casting:
Involves forming molds from sand and pouring molten metal into them. Ideal for producing large parts with simple geometries such as engine blocks and pump housings.
3. Investment Casting:
Uses wax patterns coated in ceramic slurry, which is melted away to create precise metal parts. Commonly used for aerospace components and jewelry.
4. Centrifugal Casting:
Rotates a mold at high speeds to force molten metal into its shape. Suitable for creating cylindrical parts like pipes and tubes.
5. Lost Foam Casting:
Involves molding foam patterns coated in refractory material, which vaporizes when metal is poured in, leaving the desired shape. Used for intricate designs and one-off prototypes.
6. Permanent Mold Casting:
Uses reusable molds made of metal to cast parts. Suitable for high-volume production of parts with consistent quality, like automotive wheels and engine components.
7. Plaster Casting:
Uses plaster molds to create detailed parts with fine surface finish. Often used in art and sculpture.
8. Vacuum Casting:
Utilizes vacuum pressure to draw molten metal into molds, ensuring high-quality parts with minimal porosity. Commonly used in aerospace and medical industries.
9. Continuous Casting:
Produces long, continuous metal strands or sheets by pouring molten metal into a mold. Essential for manufacturing metal sheets, rods, and wires.
10. Shell Casting:
Involves creating a shell mold by layering sand and resin, then pouring metal into it. Suitable for producing intricate parts with thin walls.
11. Pressure Die Casting:
Forces molten metal into a mold under high pressure, yielding parts with tight tolerances and fine surface finish. Used in automotive and appliance industries.
12. Squeezing Casting:
Presses molten metal into a mold cavity using hydraulic pressure. Ideal for producing small to medium-sized parts with good dimensional accuracy.
13. Low Pressure Casting:
Applies low pressure to force molten metal into molds, reducing porosity and improving part quality. Commonly used for aluminum alloy parts in aerospace and automotive industries.
14. Ductile Iron Casting:
Involves pouring molten iron into molds, producing parts with high tensile strength and ductility. Widely used in heavy machinery and construction.
15. Gravity Die Casting:
Uses gravity to fill molds with molten metal, producing parts with good dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Commonly used for automotive and marine components.
Each casting process offers unique advantages, making it suitable for different applications across industries. For more information please click the link below.