#Industry News
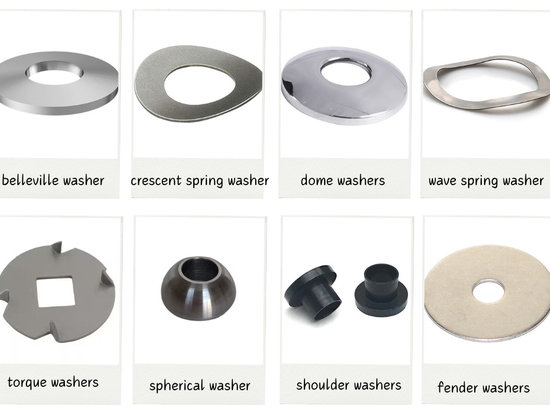
What Is Metal Embossing
preliminary understanding
Metal embossing can be achieved by matching positive and negative roller dies or by passing metal sheet or strip between rollers with the desired pattern. The principle is to use pressure to deform metal materials to form patterns or patterns. Metal embossing usually adopts two methods: cold pressing or hot pressing.
In cold pressing, the metallic material is embossed by a pair of rolling passes at room temperature. After the desired pattern is carved, the metal material is deformed by rolling to form a pattern or pattern on the metal surface.
Hot pressing is metal embossing performed at high temperatures. First, the metal material is heated to a high temperature, and then embossing rolling is used to emboss the hot metal material. Hot pressing can make metal materials deform more easily and obtain finer patterns.
The appropriate thickness of metal depends on a variety of factors, including the depth of the embossed design required, the type of metal, and the equipment and techniques used. Here are some general guidelines:
Thin Metal: For light relief or shallow designs, thin metal such as aluminum foil, brass sheets, or thin copper sheets can be used. Typically thickness ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 mm (or 0.004 to 0.020 inches).
Medium Metal: For medium depth embossing or designs, a medium thickness metal such as aluminum, copper or brass plate is suitable. Thickness ranges from 0.5 to 1.5 mm (or 0.020 to 0.060 inches).
Thick Metal: For deeper embossing or designs, thicker metals such as steel or heavy-gauge aluminum can be used. Thicknesses can range from 1.5 mm to 3 mm (or 0.060 to 0.120 inches) or even thicker, depending on the desired effect.