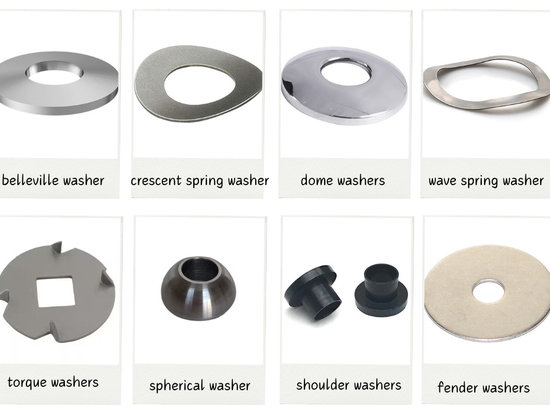
#Industry News
Aluminum Vs. Titanium Vs. Magnesium
Overview Of Aluminum, Titanium, And Magnesium Properties
Aluminum Overview
Lightweight: Aluminum is a lightweight metal with low density, suitable for applications that require weight reduction.
Good workability: Aluminum has good processing properties and is easily processed into various shapes and structures.
Good corrosion resistance: Aluminum has good corrosion resistance and can maintain stability in various environmental conditions.
Recyclability: Aluminum is a recyclable material that benefits environmental protection and resource conservation.
Lower strength: Compared with steel, aluminum has lower strength and is unsuitable for applications requiring high strength.
Prone to deformation: Aluminum has high plasticity and is prone to deformation and fatigue, limiting its application in some fields with higher mechanical performance requirements.
Titanium Overview
High strength: Titanium exhibits an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, being lighter than many other metals while possessing good strength.
Good corrosion resistance: Titanium has outstanding corrosion resistance, allowing long-term stability in harsh environments.
Biocompatibility: Titanium has good biocompatibility and is widely used in medical implants and orthopedic surgeries.
High-temperature performance: Titanium has good high-temperature performance, making it suitable for use in high-temperature environments such as aerospace and aircraft engine components.
Expensive: The production cost of titanium is high, resulting in relatively expensive prices and limiting its widespread application.
Difficult to machine: Due to its hardness and chemical stability, titanium is relatively difficult to machine and shape, requiring specialized equipment and processes.
Susceptible to oxygen absorption: Titanium is prone to oxygen absorption and oxidation at high temperatures, affecting its surface quality and machining performance.
Prone to embrittlement: Titanium is susceptible to phase transformation and oxidation at high temperatures, affecting its performance and service life.
Magnesium Overview
Low density: Magnesium is a lightweight metal with low density that is suitable for weight reduction applications.
Good workability: Magnesium has good processing properties and is easy to process into various shapes and structures.
Good thermal conductivity: Magnesium has good thermal conductivity and is suitable for applications that require good heat dissipation.
Biodegradability: Magnesium is a biodegradable, environmentally friendly material that can be used in applications such as biomedicine that require biodegradable materials.
Low strength: Compared to steel and aluminum, magnesium has lower strength and is unsuitable for applications requiring high strength.
Flammability: Magnesium is flammable in air and sensitive to flames, requiring special protective measures.
Corrosion susceptibility: Magnesium is sensitive to water and humid environments, prone to corrosion, and requires surface treatment to improve its resistance.
Expensive processing costs: Magnesium has high processing costs and is difficult to process, requiring special equipment and processes.