#Industry News
Types Of Sintering
What Is Sintering
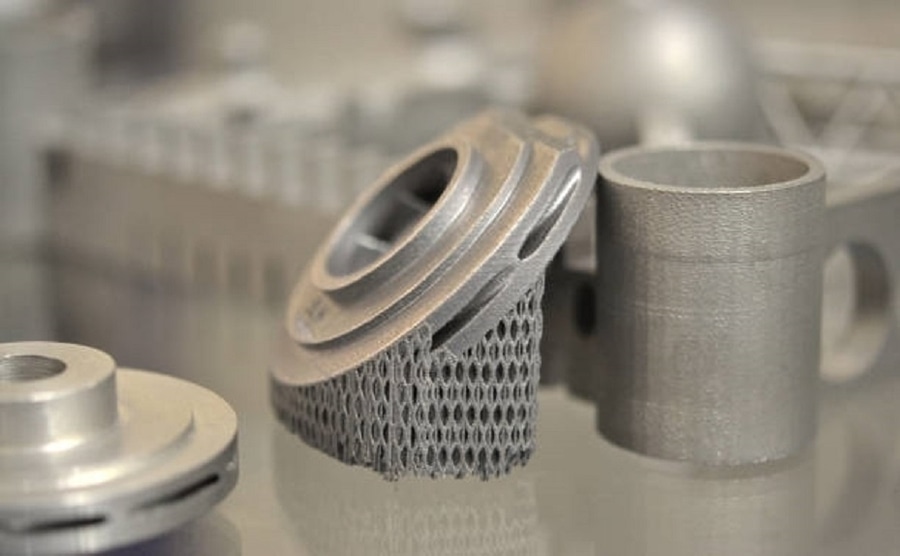
Sintering is a thermal process that allows powdered materials (usually metals or ceramics) to bond without entirely melting, resulting in a solid with enhanced strength, durability, and density.
Sintered metal refers to metal parts produced by a sintering process in which metal powders (such as steel, copper, or iron) are compacted into a mold and heated below their melting point. This method allows the manufacture of high-density, important parts with precise dimensions suitable for complex geometries such as gears, bushings, and structural components.
There are seven types of sintering:
1. Solid-state sintering: The most common type, mainly used for metals and ceramics.
2. Plastic sintering: Applied to polymers and plastics, usually for additive manufacturing or 3D printing.
3. Microwave sintering: Microwave radiation is used for heating, reducing processing time and energy consumption.
4. Spark plasma sintering (SPS): It allows for obtaining high-density results, such as nanomaterials.
5. Electric sintering forging: It combines electric current and mechanical pressure and is very suitable for manufacturing small, high-strength parts with precise tolerances.
6. Pressureless sintering: Usually under a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere, used for materials that do not require additional pressure for densification.
7. Liquid phase sintering: One component melts while the other components remain solid, usually used for composite materials.
Sintering is an efficient and versatile manufacturing process, especially when making metal parts with complex shapes and precise dimensions. For more information, please click the original text below.